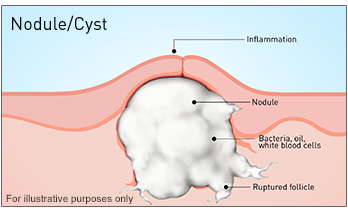
What is cystic acne, and what is the difference between nodular cysts and acne cysts? Before we get into the differences between the two, let’s talk about what causes cystic acne.
Cystic acne, like most acne, is caused by inflammation. Blackheads and whiteheads are also acne, but they are not inflammatory.
Sebaceous glands produce oil or "sebum" in our pilosebaceous unit, a compartment underneath the skin where hair grows. However, with acne, sebaceous glands often produce too much oil. That’s why inflammatory acne is common among oily skin.
What is inflammation?
Inflammation is your immune’s systems response to threats. As part of the response, your body sends out cytokines, macrophages, and white blood cells to the threatened area.
Macrophages are actually a type of white blood cell. They surround and eliminate microorganisms. They also remove dead skin cells.
Macrophages continued. What are macrophages?
Within dermatology, “the dysregulation of macrophages significantly influences the severity of inflammatory skin diseases such as acne, psoriasis, and rosacea” (Frontiers in Immunology, 2024).
Furthermore, there are two types of inflammation, acute and chronic. Acute is temporary while cystic acne is the result of chronic inflammation. More simply, inflammatory acne is chronic, meaning it perpetuates itself. Hence, sebum and dead skin cells build up, the cutibacterium acne multiplies, and waste products are formed. Then, there's inflammation, which can ultimately create more sebum.
What is nodular acne? What are pitted scars?
This is what can cause a layer of inflamed, infected tissue to surround it. Nodules need treatment from a dermatologist, and without treatment, they can persist for weeks or even months.
What is the difference between an acne cyst and a nodule?
An acne cyst is a small “sac” beneath the skin. Within the sac, there is an excessive build-up of sebum, bacteria, and dead skin cells too. Because acne cysts are filled with residue, this makes them softer, and they will eventually form a head. Then, the materials will surface onto the skin. If not treated properly, this process can cause further infection.

Photocred: Ensoul Medica Clinic
On the other hand, nodules are profoundly embedded into the skin, filled with dead skin cells and oil, and can cause considerable scarring.
Acne conglobata
What treats cystic acne?
Cystic acne requires customized treatment from a dermatologist. In some cases, dermatologists will remove the cysts or open them in addition to prescribing medication to quell the infection.
Most commonly, the dermatologist may prescribe antibiotics such astetracyclines, doxycycline, or minocycline. They may also prescribe tretinoin, which helps the skin to rapidly speed up its shedding process by binding to certain receptors. It can also train the skin to do this more quickly on its own. This can be especially helpful for cystic acne since it is deep within the skin.
In regards to scarring, tretinoin, chemical peels, lasers, or radiofrequency are common treatments as well.
Cover photo cred: Dr. Michelle Ross
Sources:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8949596/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459173/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459173/#:~:text=The%20gradual%20accumulation%20of%20keratinous,subsequent%20nodule%20formation.%5B19%5D
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11082307/